C Equity changes such as dividends, the conversion of preferred shares into common shares, and some share recapitalization that do not effect assets or liabilities The owner’s rights to the company’s assets are effectively represented by owners’ equity.
It includes all equity adjustments made between the start and conclusion of the accounting period as a result of transactions involving fixed assets, dividend payments, new capital investments, and owner withdrawals. Let’s imagine John owns a business. Travels by John Limited Owner equity for the entity is $150,000 at the start of a reporting period. Reporting Timeframe A reporting period is a month, quarter, or year during which a company’s financial statements are prepared for external use consistently over time so that the public and users may understand them. B distributions made to owners by the business. Step 1 Determine the equity value at the start of the reporting period, which must match the equity value at the conclusion of the previous reporting period. It is the equity opening balance.
Ownerfs equity example changes in equity.

Statement Of Changes In Financial Position Scfp Defined Explained Cash Flow The Balance Sheet Aro Accounting Journal Entries
There are two rulesjournal detail lines in the Owners Equity Equity rule-set. issuing fresh shares of stock. One of the four primary financial statements that the organization prepares for the conclusion of a particular accounting period, together with the balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows, is the statement of changes in equity. Depending on the performance of the, this statement often shows the entity’s capital accumulated losses or retained earnings.
illustrates the impact of revaluing fixed assets. There are many reasons for this change in net worth, including. The movement in the reserves that make up the shareholders equity is how GAAP presents the change in owners equity over the course of an accounting period.
If you examine the balance sheet of your business, it conforms to a standard accounting equation. The statement of changes in equity is a financial statement that depicts how the equity differential between a company’s assets and liabilities has changed during a specific time period. This class does not change how equity is defined or how much equity is present; it only contains modifications within equity.
Possessions and Debts ownership equity Net loss for the time period. An illustration of a condensed statement of owners equity from FINPACK illustrates how a farmer’s net worth changed over the course of a year.
The most frequent modifications to shareholders’ equity are listed below. The amount of common stock and additional paid-up capital is increased. Owners Equity is introduced.
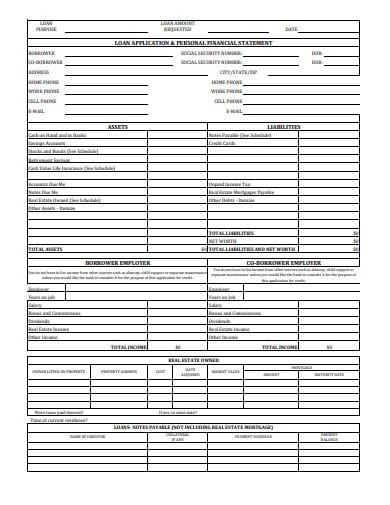
How to Prepare a Statement of Equity Changes. One of the key components of the balance sheet is owners’ equity. If a real estate project is worth $500 000 and the loan balance is $400 000, the owner equity is $400,000.
A financial statement called the statement of owners equity examines how a farmer’s net worth or owner equity changed during the previous year. The amount of owner equity in this scenario is $100,000 if a real estate project is valued at $500,000 and the loan balance is $400,000. It is what remains for the owner after all liabilities and assets have been taken into account.
Owners equity is simply the sum of the owner’s initial investment in the business less any cash withdrawals made by the owner. In the US, Statement of Changes in Equity is also known as Statement of Retained Earnings. Retained earnings go up and down.
One of the four financial statements that displays all equity changes over a given period of time is the statement of changes in equity, also known as the statement of retained earnings. It is, to put it simply, the owner’s claim to the company’s assets. Owners equity, which is displayed on the capital side of the balance sheet as the sum that belongs to the company’s owners, includes things like common stock, preferred stock, and retained earnings.
Owners equity is the sum of the owner’s initial investment in the company, the net profit or loss realized thus far, and any capital withdrawals made during the year. This sum represents the owner’s ownership interest in the company’s total capital, which the company must return to the owner following its closure. Owners equity is simply the sum of the owner’s initial investment in the business less any cash withdrawals made by the owner. This is based on the assumption that Owners Equity account adjustments that do not include Retained Earnings Current are considered to be.
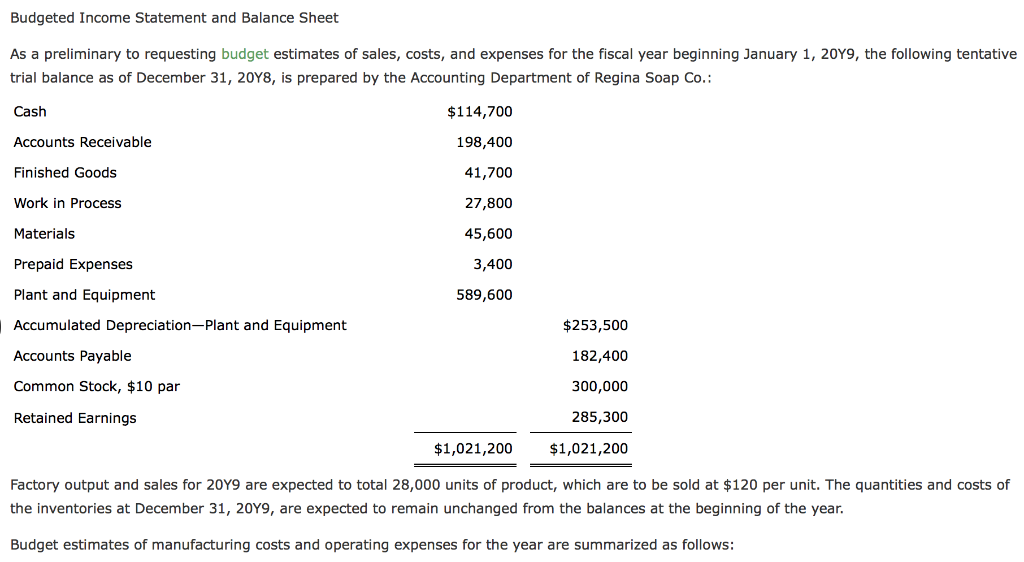
Example and Definition of Owners Equity Definition of Owners Equity It describes the difference between a company’s total assets minus its entire liabilities. Profits that have accrued, general reserves, and other reserves, etc. Step 2: Next, calculate your net income. Net Profit Direct and indirect costs are subtracted from the total in the net income formula to determine the result.
The present period Ownership is applied to the current period by this rule-set. Changes in Owners Equity excluding Current Retained Earnings.

Balance Sheet Everything About Investment Bookkeeping Business Accounting Classes And Finance Commission Received In Equation Format Of P L Appropriation Account